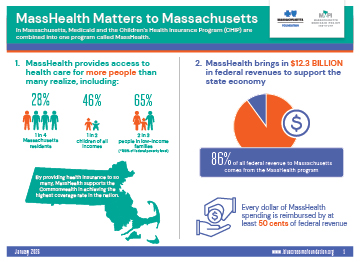
A well-functioning health care system should provide affordable and timely access to needed health care for all residents, without regard to their race, ethnicity, income, zip code, age, gender, or sexual orientation. The Massachusetts health care system, despite many exemplary qualities, does not do this, and recent access, affordability, and equity challenges for individuals and certain population groups, such as people of color, have highlighted the shortcomings of a system that is determined largely by market forces and the decisions of private entities. Given the pressures on the current system, there is a renewed interest in exploring how the process of state health planning can improve the allocation of health care resources in service to access, quality, and affordability.
This issue brief offers background on health services planning, describing the concept and outlining its history, including its rise and fall in the United States and in Massachusetts. The bulk of the brief is a catalog of the regulatory and policy tools that Massachusetts uses today that incorporate some aspects of health services planning, and how these tools do and do not interact. The brief concludes with a discussion of the gaps Massachusetts needs to fill to realize a complete, comprehensive health services planning initiative.
The Foundation hosted a webinar on Wednesday, May 28th from 11:00 AM – 12:00 PM with author, Robert Seifert, who reviewed key findings from the brief, which is intended to lay the groundwork for future research and analysis on state health planning. The webinar also featured remarks from the Massachusetts Health Policy Commission focused on the recently enacted law that established the Office of Health Resource Planning. As the name suggests, this office has a clear health planning mandate. Click here for more information on this webinar.